Bight ti Benin
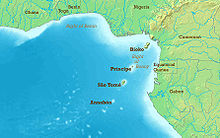
Bight ti Benin tabi Bay ti Benin ni Bight to wa ni Gulf ti Guinea ni etikun iwọ oorun ti ilẹ Afrika to gba órukọ rẹ̀ lati iṣẹdalẹ afin ti Benin[1][2].
Àgbègbè
[àtúnṣe | àtúnṣe àmìọ̀rọ̀]
Bight ti Benin tọ kasi ila oorun fun kilometres ti oji le ni ẹ̀gbẹta (400 mi) lati Cape St. Paul lọsi Nun outlet ti Niger River. Lati ila oorun o tẹsi waju lọsi Bight of Bonny (Bight ti Biafra tẹlẹ̀ri). Bight naa ni a sọ lorukọ lati órukọ afin ti ilẹ Benin[3].
Bight ti Benin gbẹkele owo oko ẹ̀ru ṣiṣe to gbajumọ lẹyin ti ijọba amunisin wọle[4]. Ounka sọpe Benin ma n ko ẹrun ẹgbẹrun kan pẹlu ẹ̀gbẹ̀fa wọle lọdun[5].
Itan
[àtúnṣe | àtúnṣe àmìọ̀rọ̀]Ni ọjọ akọkọ óṣu february,ọdun 1862 ni ijọba ti British da Bight ti Benin ti British protectorate lori akoso consul ti Bight ti Benin silẹ[6].
Bight ti Benin fun igba pipẹ ti ni aṣèpọ pẹlu oko ẹru, ibudo wọn ni a pe ni Etikun awọn Ẹru[7]. Lati Ọdun 1807 wasilẹ lẹyin ti oko ẹru ti di ewọ fun Britons, Awọn Royal Navy da squadron ti iwọ oorun Ilẹ Afrika lati palẹ oko ẹru mọ[8]. Akitiyan yi lọsiwaju si to si gboro ni ọdun 1833 nigba ti oko ẹru di ewo kakiri Igboriko ti ilẹ British[9].
| Term | Protectorate |
|---|---|
| Óṣu May, Ọdun 1852 – Ọdun 1853 | Louis Fraser |
| Ọdun 1853 – April 1859 | Benjamin Campbell |
| Óṣu April, Ọdun 1859 – Ọdun 1860 | George Brand |
| Ọdun 1860 – Óṣu January, Ọdun 1861 | Henry Hand |
| Óṣu January, Ọdun 1861 – May 1861 | Henry Grant Foote |
| Óṣu May, Ọdun 1861 – 6 August 1861 | William McCoskry (acting) |
Ni ọjọ kẹfa, Óṣu August, Ọdun 1861 ni Bight ti Biafra protectorate ati Bight ti Benin protectorate darapọ lati di united British protectorate to pada dapọ lati ilẹ Naijiria[10].
Itọkasi
[àtúnṣe | àtúnṣe àmìọ̀rọ̀]- ↑ "West African Coast, Slave Trade, Colonialism". Encyclopedia Britannica. 1998-07-20. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ Almar, R.; Kestenare, E.; Reyns, J.; Jouanno, J.; Anthony, E.J.; Laibi, R.; Hemer, M.; Du Penhoat, Y. et al. (2015). "Response of the Bight of Benin (Gulf of Guinea, West Africa) coastline to anthropogenic and natural forcing, Part1: Wave climate variability and impacts on the longshore sediment transport". Continental Shelf Research (Elsevier BV) 110: 48–59.
- ↑ "Bight of Benin". Encyclopedia of World Geography. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ "Verger, Pierre, Trade Relations Between the Bight of Benin and Bahia, 17th to 19th Century (Ibadan: University of Ibadan Press, 1976), 421-423, 568-575. · Slavery Images". Welcome · Slavery Images. 2020-12-08. Archived from the original on 2023-08-24. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ "Bight of Benin transatlantic slave trade". Slave Voyages. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ "Bight of Benin Protectorate". segundawodu.com. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ "Republic of Benin". New World Encyclopedia. 1960-08-01. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ Brain, Jessica (2023-03-10). "The West Africa Squadron". Historic UK. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ (IHR), Institute of Historical Research; London, University of; York, University of. "Chasing Freedom: the Royal Navy and the suppression of the transatlantic slave trade, an exhibition review". IHR Web Archives. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
- ↑ Dike, K. O. (1956). "JOHN BEECROFT, 1790—1854: Her Brittanic Majesty's Consul to the Bights of Benin and Biafra 1849—1854". Journal of the Historical Society of Nigeria (Historical Society of Nigeria) 1 (1): 5–14. http://www.jstor.org/stable/41856608. Retrieved 2023-08-24.
